Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (pNENs) account for approximately 3%-5% of pancreatic tumors. Based on hormone secretion status, pNENs are classified into functional and nonfunctional types, with functional pNENs comprising about 10%-30% of cases. The most common functional pNENs include insulinomas and gastrinomas, while other functional subtypes encompass somatostatinomas, glucagonomas, and VIPomas (vasoactive intestinal peptide-producing tumors). Functional pNENs are named according to the predominant hormone they secrete.
With the widespread application of advanced imaging techniques, the detection rate of nonfunctional pNENs has significantly increased. The differentiation of pNENs primarily relies on immunohistochemical staining to identify specific biomarkers.
Grading is based on the degree of tissue differentiation and cell proliferative activity. Staging of pNENs is recommended to follow the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) 8th Edition TNM staging system.
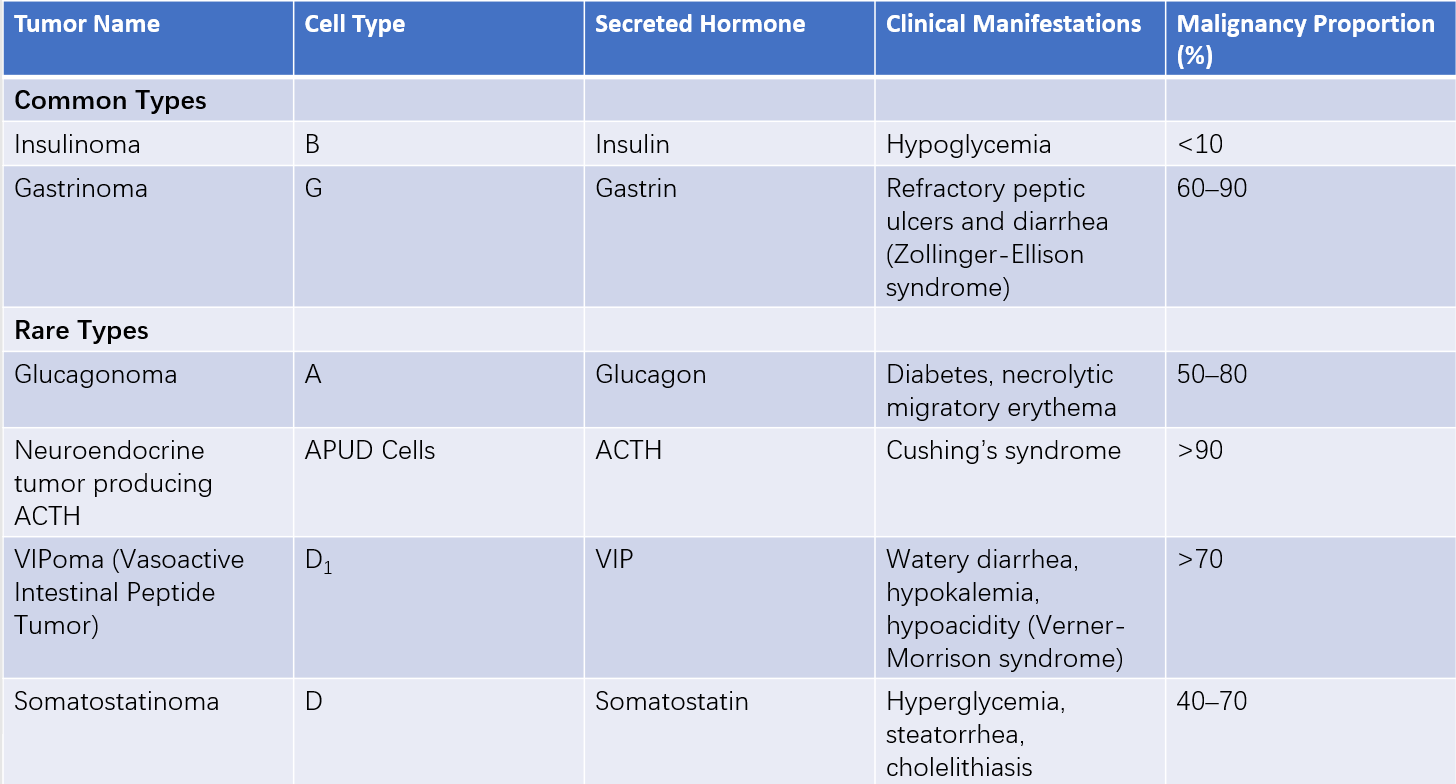
Table 1 Classification of functional pNENs
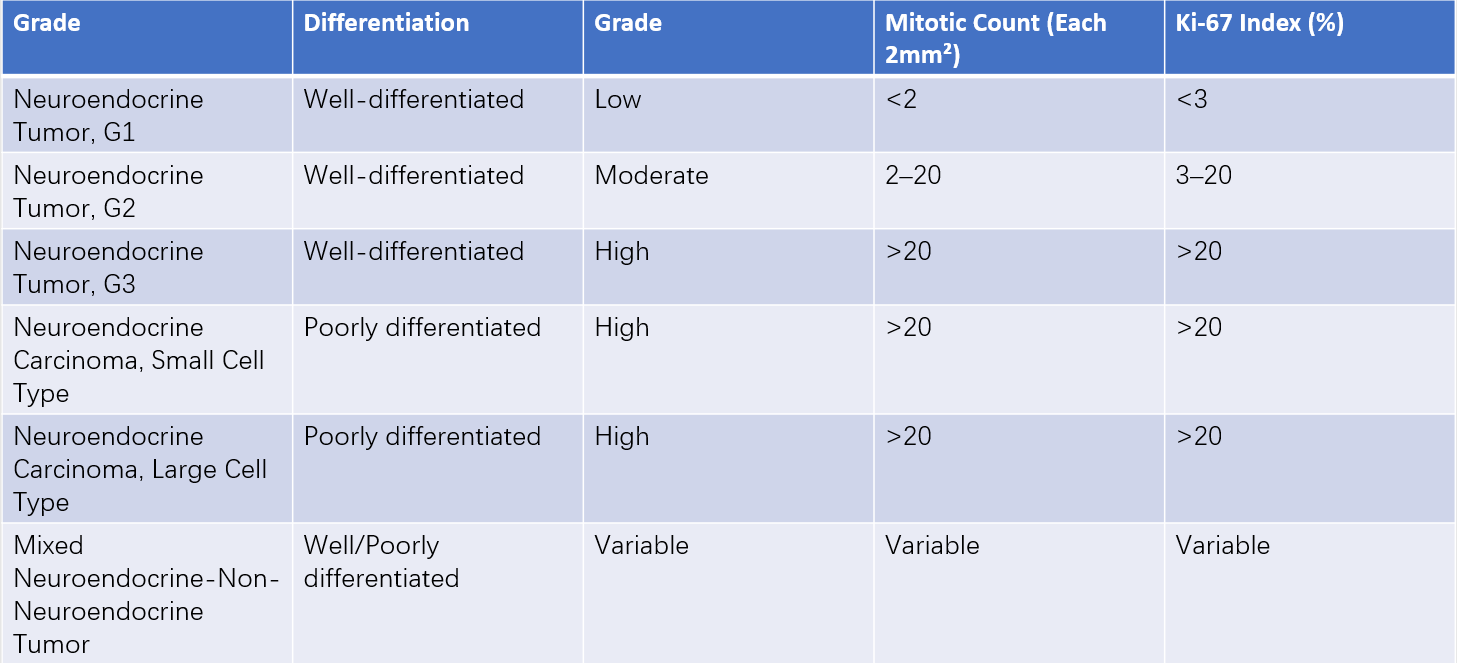
Table 2 Grading criteria for pNENs

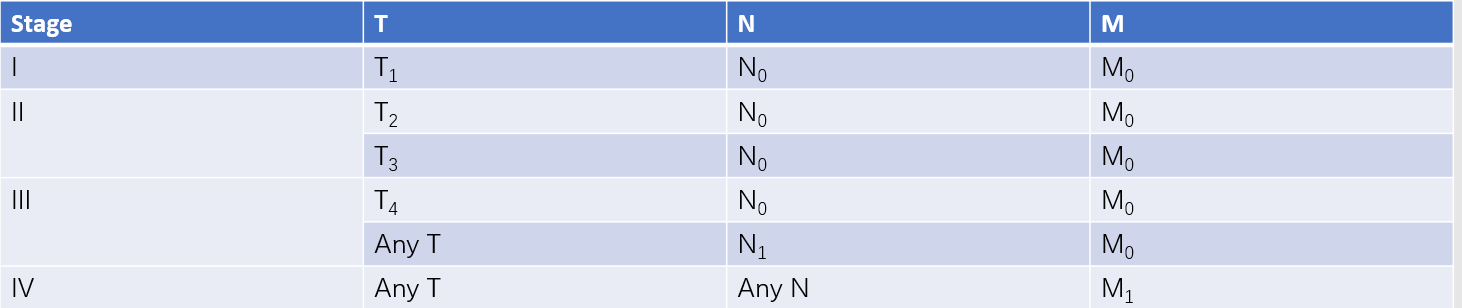
Table 3 AJCC 8th edition TNM staging system
To be continued